Pill-E: Pill-Dispensing Robot
Sep 2022
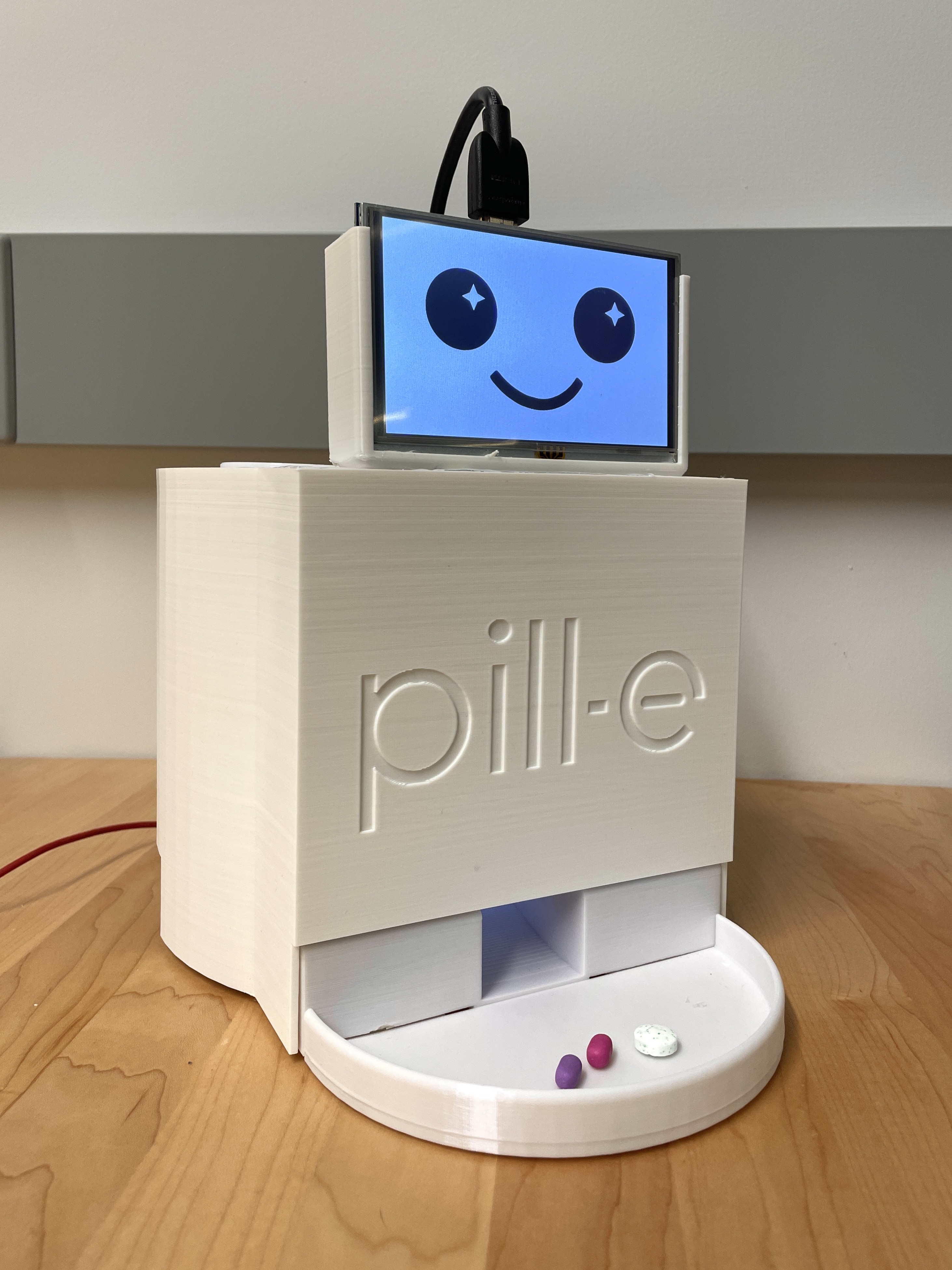

Description
Pill-E is an automated desktop medication management system designed to improve medication adherence through engaging human-robot interaction. Developed as a capstone project during my high school years, Pill-E combines mechanical dispensing mechanisms, computer vision, and affective computing to create a socially assistive robot that helps users maintain consistent medication schedules.
Medication non-adherence affects an estimated 50% of patients with chronic conditions, leading to $100-300 billion annually in preventable healthcare costs. Pill-E addresses this challenge by transforming routine medication intake from a tedious task into a positive interaction with an emotionally responsive companion.
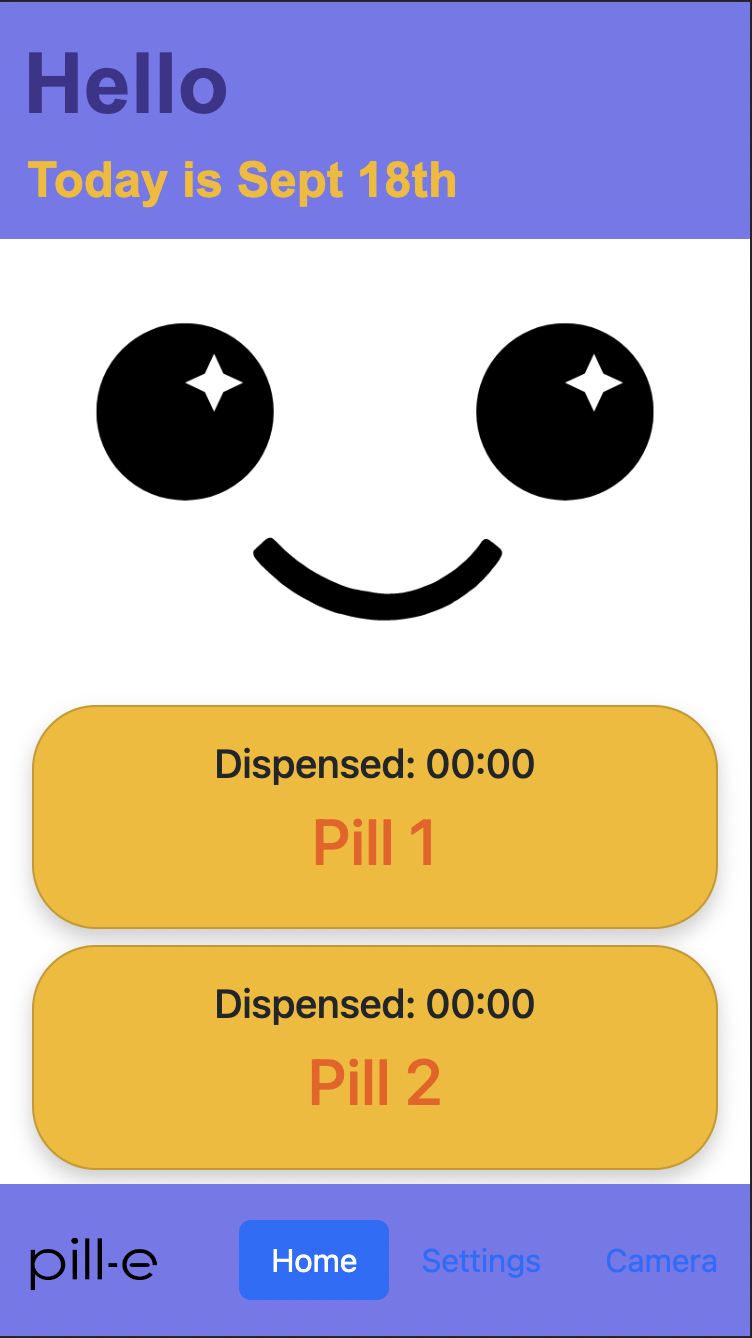
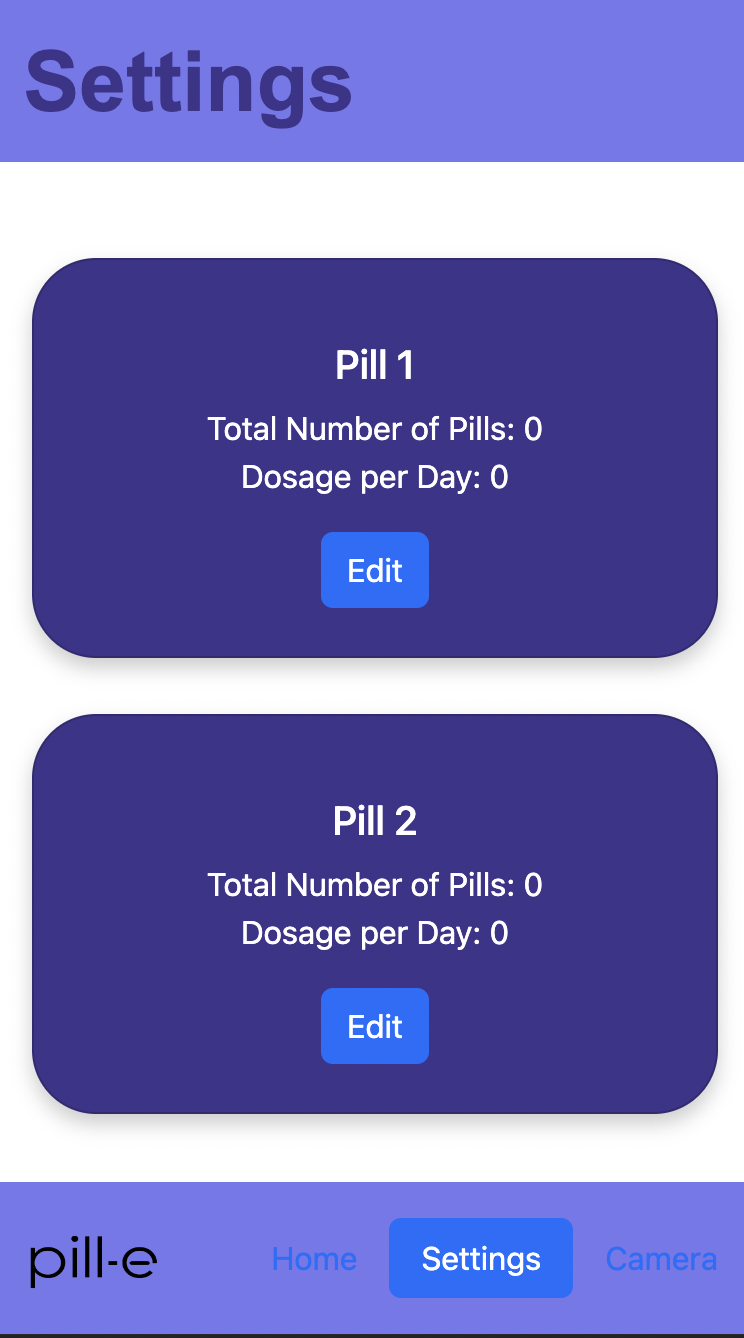
System Architecture
Hardware Components
- Dispensing Mechanism: Rotating carousel with 7 pill compartments, each holding up to 30 standard tablets. Stepper motor-driven indexing (NEMA 17, 200 steps/rev with 1/8 microstepping) provides precise compartment alignment beneath dispense chute.
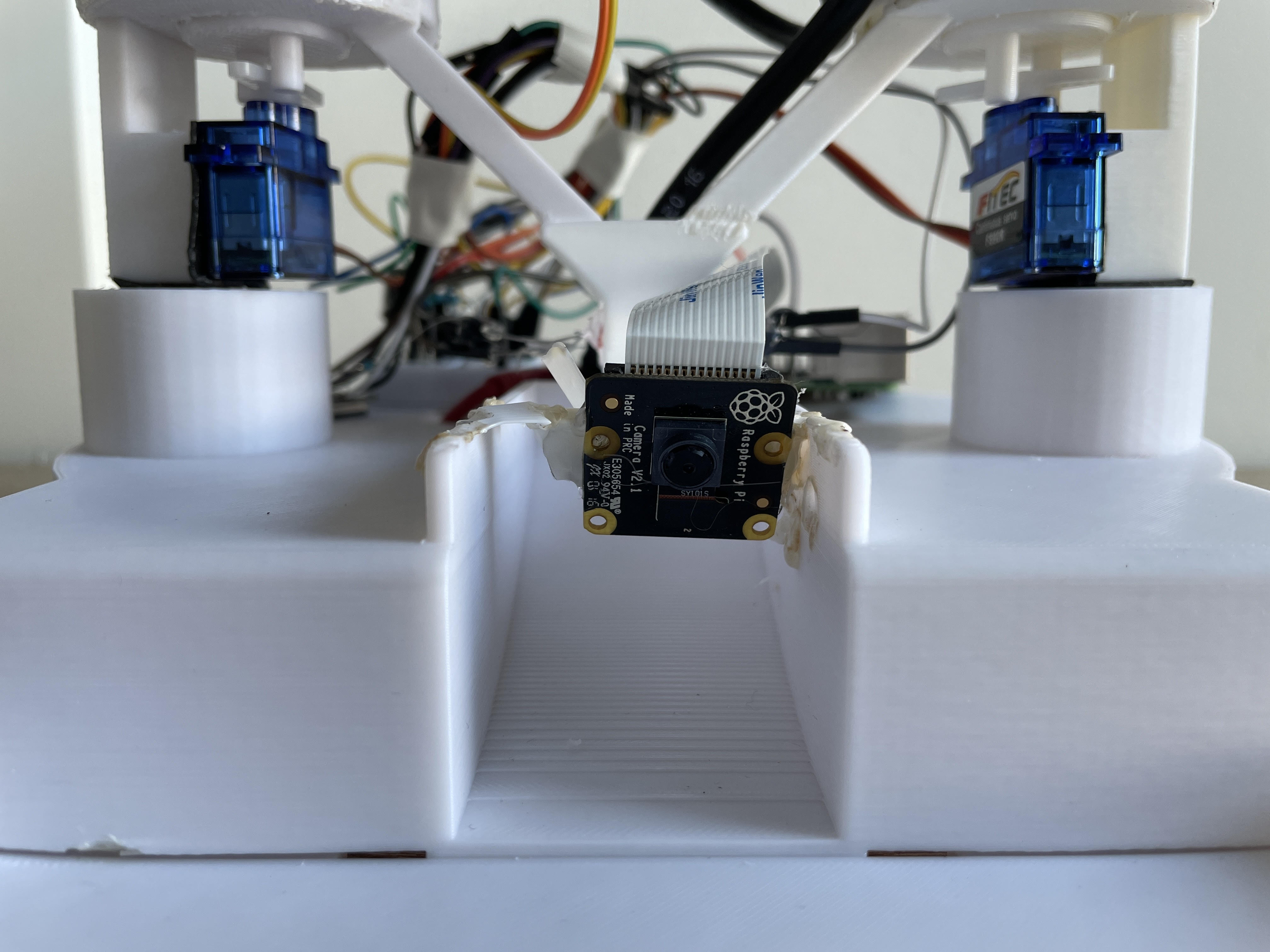
- Computer Vision System: Raspberry Pi Camera Module v2 (8MP, 1080p) positioned beneath dispense aperture for pill detection and count verification. OpenCV-based image processing pipeline detects dispensed pills via background subtraction and contour analysis.
- Display Interface: 7-inch capacitive touchscreen (800×480 resolution) running custom Qt/QML interface for medication schedule display, manual dispense controls, and robot emotion visualization.
- Actuated Expressions: Servo-driven mechanical eyelids (2× SG90 micro servos) enable blink animations and emotional state communication through lid position and movement dynamics.
- Audio Feedback: 3W speaker for voice prompts, confirmation sounds, and ambient interaction sounds (generated via Festival text-to-speech engine).
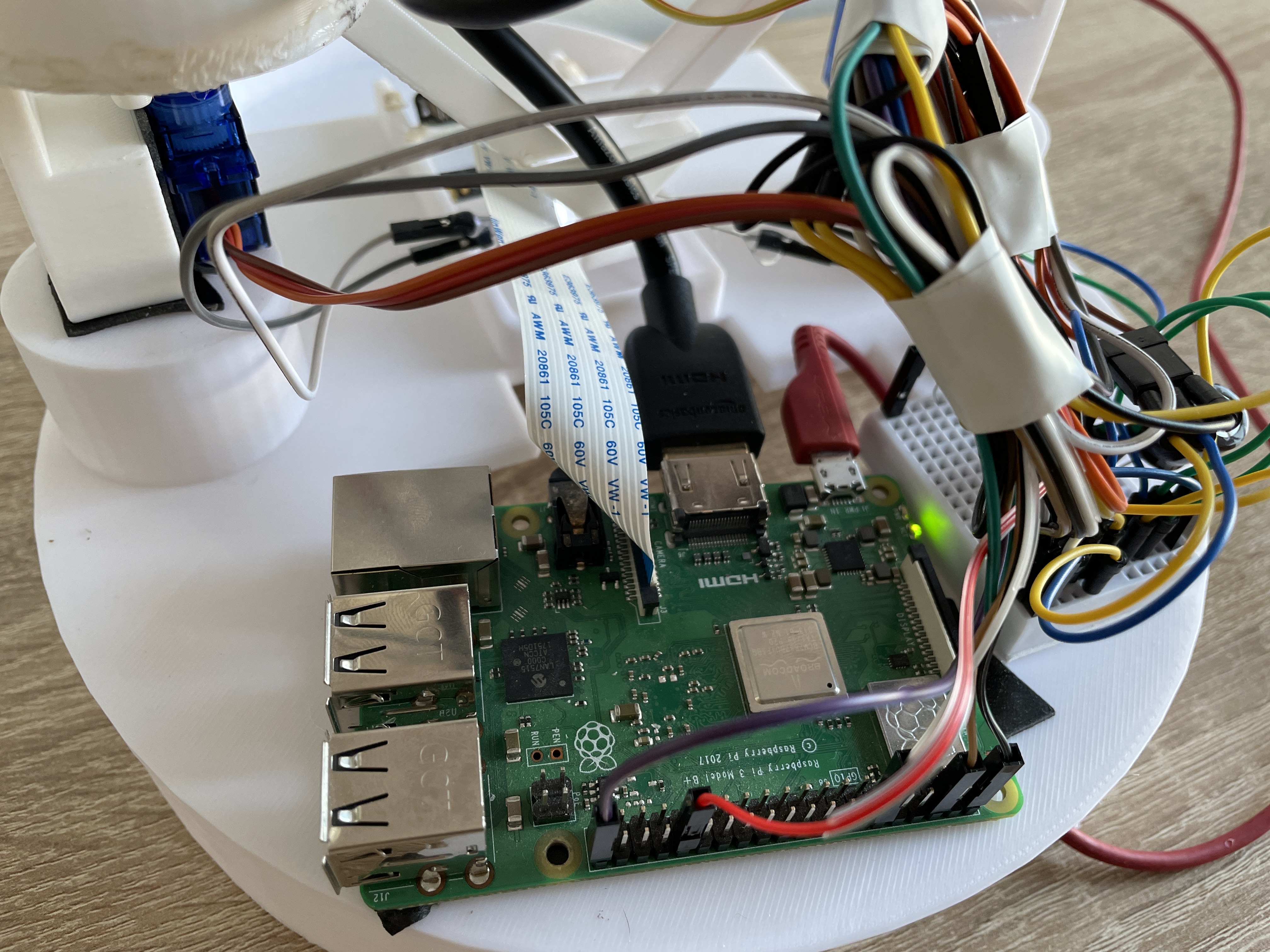
- Processing: Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (4GB RAM) running custom Python application stack with real-time scheduling daemon and web server for mobile app communication.
Software Architecture
- Backend: Python 3.9 with Flask REST API framework for mobile app synchronization, SQLite database for medication schedules and adherence history
- Frontend: React Native mobile app (iOS/Android) with Firebase Cloud Messaging for push notification reminders
- Computer Vision: OpenCV 4.5 with custom pill detection pipeline (HSV color space filtering, morphological operations, connected component analysis)
- Scheduling Engine: APScheduler library with cron-like expressions for flexible dosing intervals (e.g., "every 8 hours", "twice daily with meals")
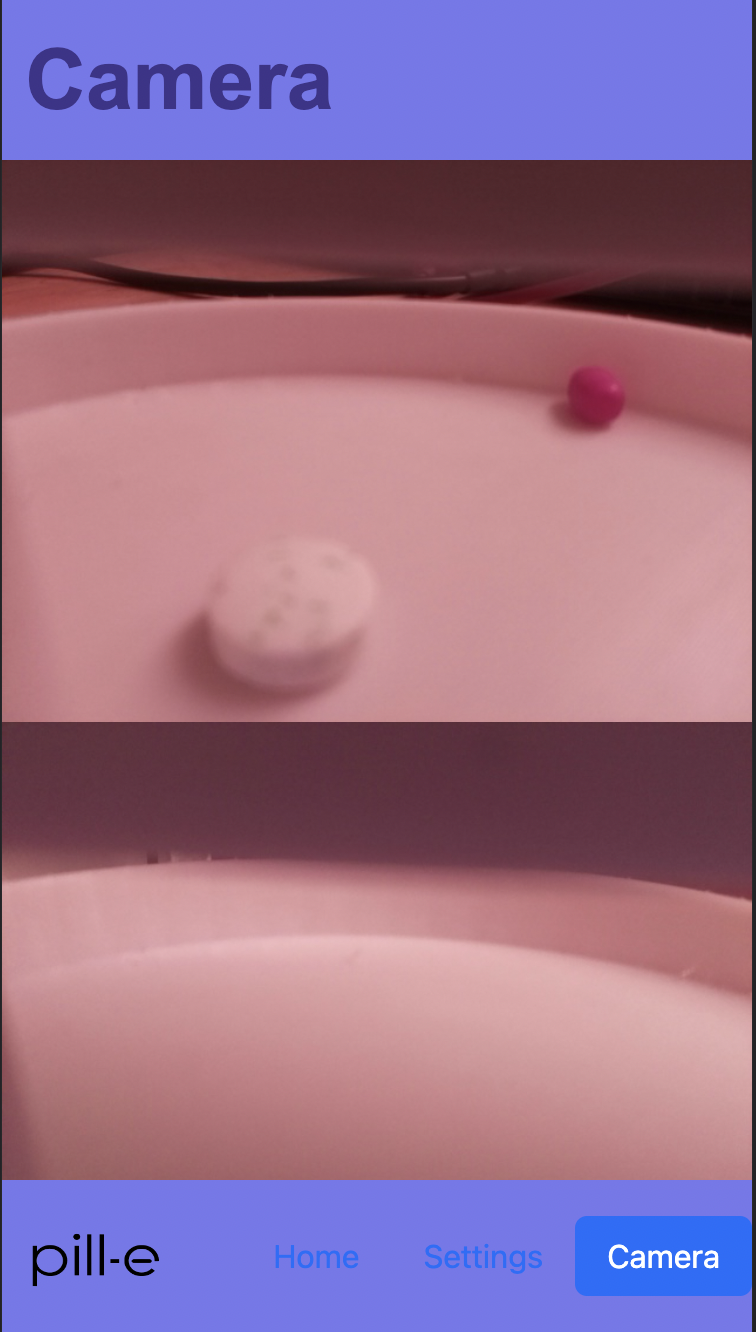
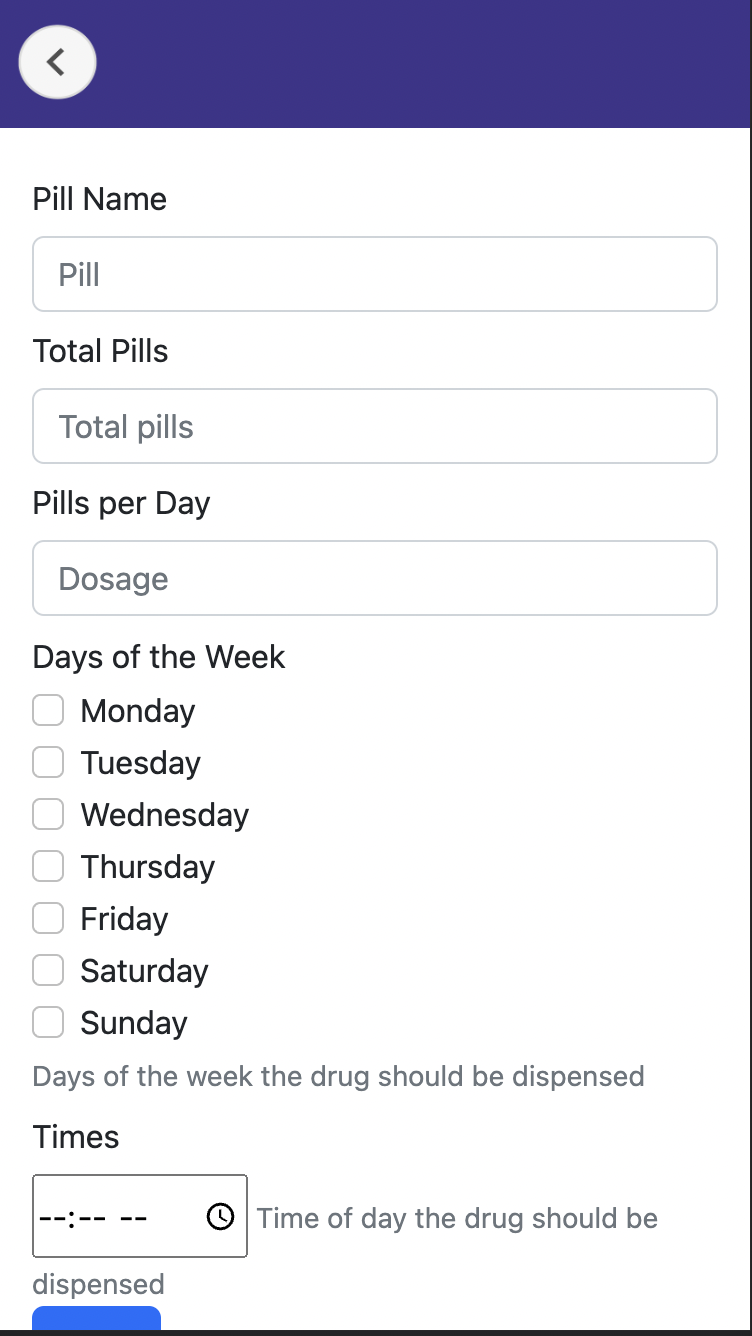

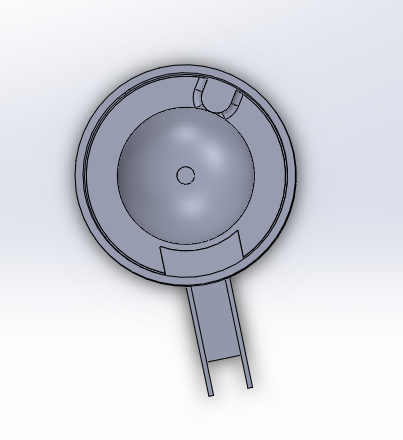
Mechanical Design
Dispenser Architecture
The carousel dispenser employs a gravity-fed single-pill release mechanism inspired by bulk vending machines:
- Compartment Geometry: Each compartment features a tapered funnel (45° angle) leading to a gated aperture (8mm × 8mm opening). Pill stack height ≤ 50mm to prevent jamming under self-weight.
- Gate Mechanism: Solenoid-actuated sliding gate (5V, 0.5A pull) opens aperture for 800ms ± 50ms to release single pill. Gate timing calibrated experimentally for common tablet geometries (aspirin, ibuprofen, multivitamins).
- Indexing Precision: Optical interrupter sensor (ITR9608, 940nm IR LED + phototransistor) detects carousel home position. Hall effect sensor confirms stepper motor position between dispenses to detect skipped steps.
- Pill Detection: Camera positioned 12cm below dispense chute with 45° angled mirror for top-down pill imaging. Computer vision confirms pill count (1 pill dispensed = success, 0 = jam/empty, 2+ = double-dispense error).
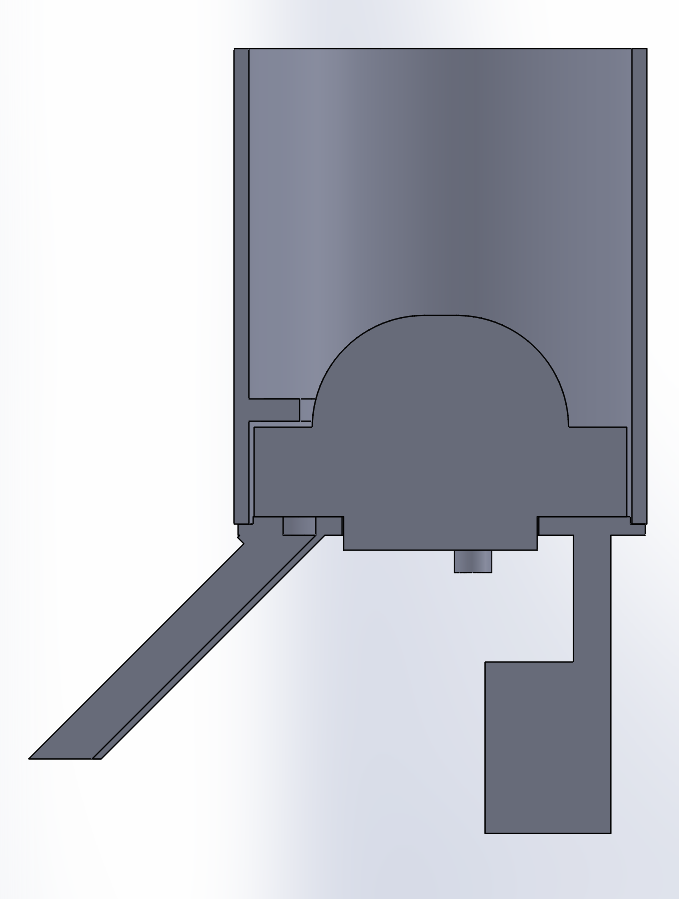
Internal Systems Integration
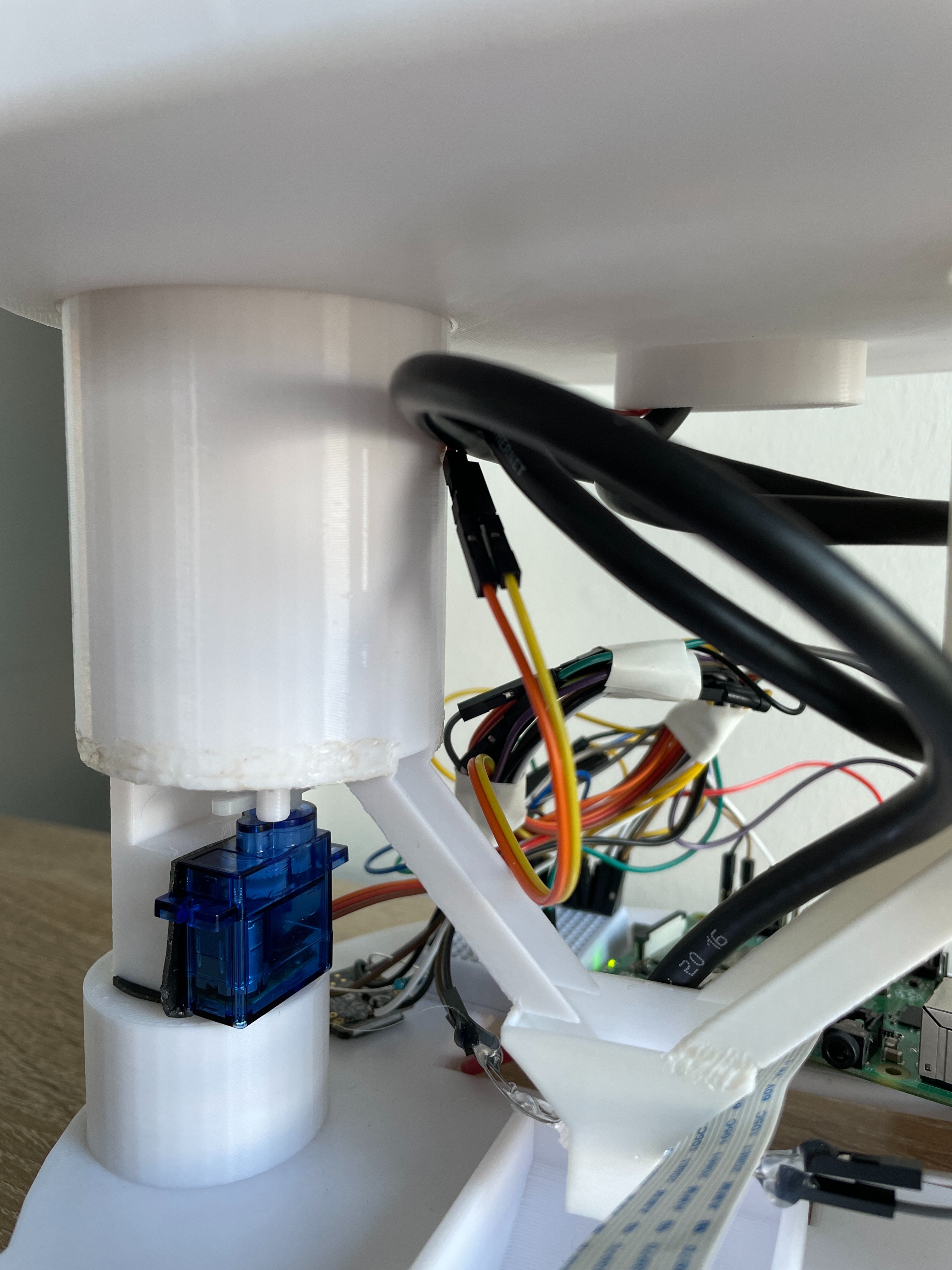
Electronics Layout
Custom PCB integrates power distribution, motor drivers, and sensor interfaces:
- Power System: 5V/3A USB-C input, dual LDO regulators (3.3V for logic, 5V for servos/solenoid), overcurrent protection via PTC resettable fuses
- Motor Control: A4988 stepper driver with current limiting (0.8A per phase), microstepping configuration via GPIO jumpers
- Sensor Interfaces: I2C bus for optional environmental sensors (temperature, humidity for pill storage monitoring), GPIO expander (MCP23017) for 16 additional digital I/O
- Emergency Stop: Physical button triggers interrupt to halt all actuators and enter safe state (gate closed, carousel locked)

Affective Computing & Social Interaction
Emotional Expression Design
Pill-E employs minimalist mechanical animation to communicate internal state and build rapport:
- Idle State: Slow periodic blinks (0.3 Hz, 200ms close duration) with subtle eyelid droop during extended idle periods to convey "sleepiness"
- Medication Reminder: Rapid excited blinks (2 Hz, 3 cycles) followed by wide-open "alert" expression, accompanied by cheerful chime audio
- Successful Dispense: Slow satisfied blink (400ms duration) with upward lid curve to mimic smile, synchronized with positive voice feedback ("Well done!")
- Error State: Asymmetric lid positions (one eye partially closed) with intermittent rapid blinks to signal "confusion", paired with apologetic voice prompt
Adherence Gamification
Mobile app implements behavioral reinforcement strategies to sustain engagement:
- Streak Tracking: Consecutive days without missed doses displayed prominently, with milestone badges (7-day, 30-day, 90-day streaks)
- Progress Visualization: Calendar heatmap showing adherence history, colored by on-time (green), late (yellow), or missed (red) doses
- Social Accountability: Optional sharing of adherence statistics with designated caregiver/family member for gentle peer pressure
- Reward System: Unlock custom robot personalities and voice packs upon achieving adherence milestones

User Testing & Results
Pilot Study Protocol
Conducted 4-week user study with 8 participants (ages 22-67, mean 44 years) managing chronic conditions requiring daily medication:
- Baseline Period: 1 week self-reported adherence tracking without Pill-E intervention
- Intervention Period: 3 weeks using Pill-E for medication reminders and dispensing
- Metrics: Adherence rate (% doses taken on schedule ± 1 hour), subjective usability (System Usability Scale questionnaire), qualitative feedback via semi-structured interviews
Key Findings
- Adherence Improvement: Mean adherence increased from 73% ± 18% (baseline) to 91% ± 9% (intervention), statistically significant improvement (paired t-test, p < 0.01)
- Usability: Average SUS score 78.5 (Grade B, "Good" usability), participants praised intuitive mobile app but noted occasional pill jamming in dispenser
- Engagement Sustainability: Adherence remained stable throughout 3-week period (no week-over-week decline), suggesting novelty effect did not dominate
- Emotional Response: 6/8 participants reported forming "attachment" to robot, describing it using terms like "helpful companion" and "my little medication buddy"
Failure Mode Analysis
- Pill Jamming: Occurred in 3.2% of dispense attempts, primarily with oblong tablets (aspect ratio > 2:1). Solution: Increase gate aperture to 10mm × 8mm
- False Positive Detection: Computer vision occasionally detected shadows as pills in low ambient light. Solution: Add active LED ring illumination beneath chute
- Network Connectivity: Mobile app push notifications failed when home WiFi dropped. Solution: Implement local Bluetooth fallback for proximity-based alerts
Future Development
Technical Enhancements
- Multi-Pill Dispense: Redesign gate mechanism to reliably dispense 1-4 pills simultaneously for multi-medication regimens
- Pharmacy Integration: API connection to electronic health records (EHR) for automatic schedule synchronization upon prescription refill
- Medication Identification: Train convolutional neural network (CNN) on NIH pill image dataset to verify correct medication dispensed via imprint/color recognition
- Environmental Sensing: Monitor storage temperature/humidity to alert user if medication storage conditions exceed pharmaceutical stability ranges
Expanded Applications
- Pediatric Medication: Gamified robot personality for children's adherence, integration with parent dashboard for supervision
- Elderly Care: Larger display, voice-controlled interface, automatic caregiver notification for missed doses
- Clinical Settings: Multi-patient carousel dispenser for assisted living facilities, integration with electronic medication administration records (eMAR)
Commercialization Pathway
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM) analysis to reduce BOM cost from $180 (prototype) to target <$80 (volume production)
- FDA regulatory assessment (likely Class I or II medical device depending on diagnostic claims)
- Insurance reimbursement coding (CPE1 for remote patient monitoring durable medical equipment)
- Partnership with pharmaceutical companies for medication adherence programs and patient support initiatives